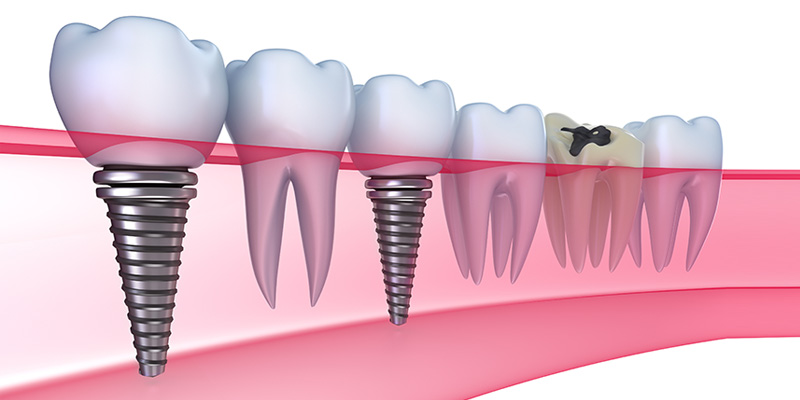
Any kind of artificial substance which is planted into the human body is called “implant”. Dental implants, on the other hand, are artificial roots of teeth made from titanium, which are planted into the jawbone and used for the purpose of providing the function and aesthetics of missing teeth. Dental implants are being used since 1965. Thanks to the technological advancements in the last 20 years, the success rates have substantially risen up to 98%.
Being a part of facial aesthetics, the loss of teeth causes psychological and social issues as well as problems in nutrition, digestion and speech disorders.
Teeth loss can be treated by classic methods via bridge prostheses connected to your natural teeth or removable dentures, as well as implant supported prostheses. In the case of single or more missing teeth, if there is enough amounts of bone fit for implants and if the patient’s health and condition and oral care allows it, implant treatments can be applied.
Under what circumstances can implants be applied?
Single tooth loss (or more): It’s a type of treatment where the lost teeth is replaced by a single implant. If there is more than one lost teeth, more number of implants can be used for treatment.
Total edentulism: If there is no teeth left and the patient can not use prostheses due to the faucial reflex or inadequate amount of prosthesis integrity in the oral cavity, there are two ways to do implant supported prostheses. For removable prostheses, two or four implants may be placed for the purpose of supporting the prosthesis from underneath and improve their retention, The second method is if the amount of implants are increased to a number such as six or eight implants, fixed prostheses can be used without the need of removable ones.
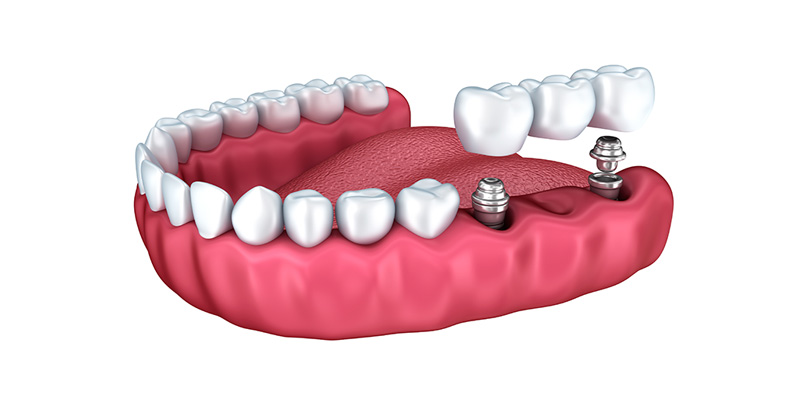
How is the structure of the implant?
Titanium, which is used in manufacturing implants, are quite durable and considered as compatible with the tissue by the body. Because of being one of the most biologically compatible substances with the body, the chances of an allergy are very slim and this minimizes the reactions of the body against foreign substances.
What is the process of implant application?
After the clinical and radiographical examination is performed, the dentist examines whether the patient has favorable width and depth on the jawbone and the gingiva in order to place specific length and diameter of implants. If your dentist deems necessary, he may wish to perform a more detailed examination. For example; if your dentist wishes to examine the surgical area's bone tissue in a more detailed manner, he may request a tomography. If the patient has systemic illnesses or bone loss, he may request a blood panel as well. Then the dentist explains the implant planning and the prostheses which will be used to his patient. After getting approval, the surgery stage begins.
Implant operation is a surgical procedure which is performed under local anesthesia. In this procedure, the gum tissue is lifted away from the bone, a socket is opened with a drill of special size in order to accommodate the implant's diameter and the implant is placed into this socket. Afterwards, the gum tissue is closed with stitching. Thanks to the local anesthesia used in the procedure, patients feel no pain during the procedure. After the operation, a mild pain and swelling can be experienced as much as after a routine tooth extraction. These kind of effects can be remedied by applying pressure with ice and painkillers. The implants are given a certain amount of time to get attached to the bone surface. After this time, the upper structure is prepared. Temporary prostheses are used after the procedure till the permanent prostheses are made.
After the healing period, the dental professional attaches the prosthesis part to the implant, thereby establishing a structure which is connected to the stable structure placed inside the bone that identically imitates the natural tooth. The prosthesis stage is completed by performing the necessary operations on this structure for either the stationary or removable prosthesis. After the procedure, the patient is usually given 3-6 months’ time in order for the implant and the teeth to merge (osseointegration). However, implants manufactured in recent years allow for beginning the prosthesis preparation immediately without waiting for a firm attachment (primary stabilization) inside the bone.
The anatomic features called sinus cavities on upper jaw and mandibular canal on lower jaw may limit the depth for implantation or the horizontal depth of the jaw may not be enough for the diameter of the implant. In cases like this, advanced surgical techniques are used to reinforce bone tissue. The dentist may consult with his patient for performing advanced surgical technique. In these cases, before the implant is placed, bone tissue reinforcement procedures are performed and implant may be placed during or after the procedure. The waiting period can be extended due to these surgical procedures.
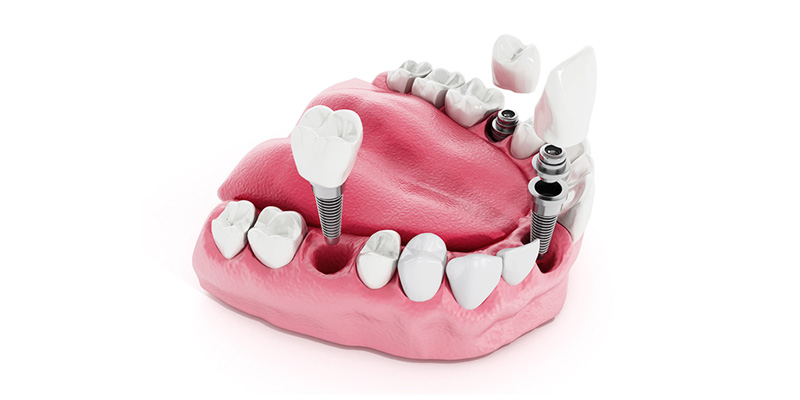
Post-Operation Oral Health Care
For the success and prolonged use of the implants, proper oral care and regular controls are the most important conditions. Neglecting oral hygiene, excessive consumption of alcohol and cigarettes will adversely affect the success of the implants. In order to prevent this, patients must take heed of dental professional’s advice and keep a regular schedule for their appointments.
Can implants be applied to everyone?
In order for implants to be applied, bone development in patients (ages 16-17 in females, 18 in males) has to be completed. There is no age limit in adults. Patients of varying ages can be treated with implants provided that they have a good general health and adequate bone structure.
Can implants be rejected by the body?
Implants are made from titanium and biologically compatible materials. Because titanium is not a living substance, it doesn't cause any kind of antigen-antibody reaction and therefore there is no "tissue rejection".
Conditions where the implants can not be applied
- On people with systemic diseases
- On patients with irregular and uncontrolled diabetes
- Under circumstances where the bone structure is inadequate and anatomically risky for the patient
- Situations where the patient will not be able to maintain their oral hygiene properly after the operation
What Factors Do The Implant Treatment Success Depend On?
For success of the implant treatment, the systemic condition of the patient and the patient's general health must not include any factors which would be an obstacle for implantation. The bone around the surgical area must be in appropriate width and length. (In cases of inadequate width and length, special methods such as bone grafts and membranes can be utilized to place implants)
The patient's smoking and alcohol consumption is important. It is recommended to quit these habits altogether if possible. If not, reduction is recommended.
In the success of implant treatment, the role of the patient is also crucial. Just as a patient with poor oral hygiene can lose his teeth and gingiva's health, implants also can be lost in the same manner. Therefore, patients who are going through implant treatment must perform their dental care with maximum thoroughness. It is important to keep in mind that getting the implants placed won't get the job done and routine controls are essential.
After the implants are placed and the waiting period is over, the right time to call the treatment successful is when the superstructures with porcelain crowns are placed and there is load on the implant. The health state of the bone and the gingiva around the implant is the harbinger of healthily retaining the implant in the mouth.

 Türkçe
Türkçe English
English Français
Français русский
русский Español
Español